Technical Advice and Support
Fuel & Tank Expertise
Technical Advice from JWH Tanks
Navigating the complexities of fuel management can be challenging. With decades of experience serving diverse industries, JWH Tanks provides expert technical advice and comprehensive solutions to ensure the smooth operation of your fuel systems, control risks, and ensure regulatory compliance. We’re here to help you avoid costly downtime, environmental issues and operational inefficiencies.
Our team of experienced technical advisors is available to provide specialist guidance on all aspects of fuel and tank management. Whether you’re dealing with contamination, planning a new installation, or seeking routine maintenance advice, we’re just a phone call away.
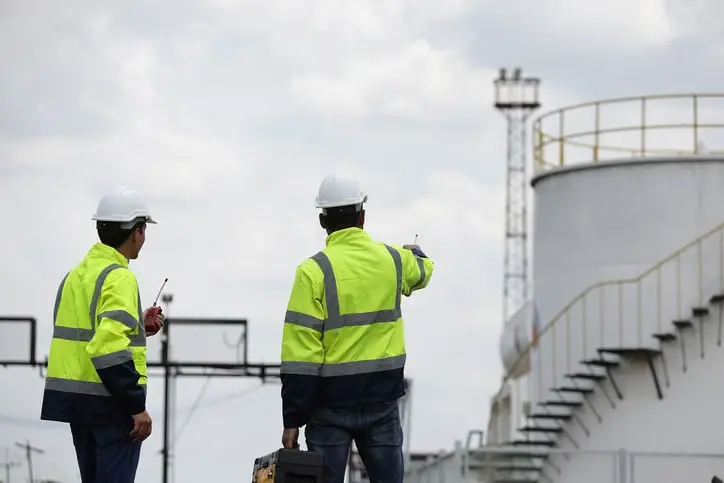

Turnkey Fuel Solutions: Expertise, Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
We offer expertise and rapid, efficient service across a wide range of industries. We provide complete turnkey solutions tailored to your needs, using cutting-edge equipment and best practices for cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
Our Technical Advisory Services Cover:
- Fuel Contamination: Suspect contaminated fuel? Our experts can guide you through the process, from initial assessment and testing to remediation and preventative measures. We'll help you understand the risks and choose the most effective solution.
- Fuel Polishing & Filtration: We can assess your fuel system and recommend the most cost-effective cleaning and filtration solutions to maintain fuel quality and prevent costly equipment failures.
- Fuel Transfer & Uplift: Planning a fuel transfer or uplift? Our specialists can provide technical advice on best practices, safe handling procedures, regulatory compliance and cost considerations.
- Tank Installations: Choosing the right tank is crucial. Our advisors can provide up-to-date guidance on tank selection, installation regulations, and best practices to ensure a safe and compliant installation.
- Tank Cleaning: Regular tank cleaning is essential for fuel quality and environmental protection. We can advise on appropriate cleaning schedules, methods and the importance of maintaining tank hygiene.
- Tank Testing & Inspection: Ensure the integrity of your tanks with regular testing and inspection. Our team can explain the different testing methods available and help you schedule inspections to prevent leaks and contamination.
- Tank Decommissioning: Decommissioning a fuel tank requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. Our experts can guide you through the process, ensuring a safe and compliant decommissioning project.
Your Needs, Our Priority: Delivering Exceptional Service and Customised Solutions
JWH is committed to providing exceptional service and building long-term relationships with our clients. Our experienced team provides tailored solutions that meet your specific needs.
Why Choose Us?
- Decades of Experience: Over 50 years of experience in the fuel industry.
- Expert Team: Highly qualified engineers and technical advisors working to our ISO certified management system.
- Comprehensive Solutions: From testing and analysis to tank installations and decommissioning, we offer a complete range of services.
- Commitment to Quality: We guarantee our services and stand behind our work.
- Focus on Customer Satisfaction: Your needs are our priority.
JWH Tanks are proud to be members of associations such as the Association for Petroleum & Explosives Administration, Petroleum Equipment Installation & Maintenance Federation and The Oil Firing Technical Association (OFTEC).
Contact us today on 0113 263 5163 or request a quote online. Let us help you get the most from your fuel systems and ensure peace of mind.
Tank Services Technical Advice FAQs
Bulk oil storage on commercial sites in the UK is governed by strict regulations. Key considerations include:
- Capacity: Regulations vary depending on the total storage capacity. Larger installations require more stringent controls.
- Containment: Secondary containment (bunding) is essential and must meet specific standards.
- Location: Tank placement must comply with separation distances from buildings, boundaries, and process environments. Fire safety regulations are paramount.
- Construction and Materials: Tanks must be constructed of suitable materials and meet British Standards. Regular inspection and testing are required.
- Environmental Permits: Depending on the storage volume and location, you may need an environmental permit from the Environment Agency.
- Security: Secure storage is essential to prevent theft and vandalism.
- Planning Permission: Planning permission can sometimes be required for new bulk storage installations.
GOV.UK (Oil Storage): A good starting point for finding government information on oil storage regulations: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/storing-oil-at-a-home-or-business
Commercial oil storage in the UK is subject to various environmental regulations, primarily enforced by the Environment Agency. These regulations cover:
- Pollution Prevention: Preventing spills and leaks is crucial. Robust secondary containment and leak detection systems are essential.
- Groundwater Protection: Regulations aim to protect groundwater from contamination. Proper tank siting and bunding are critical.
- Waste Disposal: Waste oil and tank cleaning materials must be disposed of by licensed waste carriers.
- Reporting: You may need to report spills or leaks to the Environment Agency.
- Oil Storage Regulations: Specific regulations cover the design, construction, and operation of oil storage facilities.
For information on environmental regulations related to pollution prevention, see the below link. https://www.gov.uk/guidance/pollution-prevention-for-businesses
Regular inspection and testing are mandatory for commercial oil tanks in the UK. The frequency depends on the tank’s size, age, and construction. We recommend following OFTEC guidelines, GEP (Good Engineering Practice) and EEMUA guidelines where applicable. Speak with a qualified technician to establish a suitable inspection and testing schedule. This should include regular visual inspections, as well as more in-depth testing methods as required.
Decommissioning a commercial oil tank requires careful planning and adherence to strict regulations. Key steps include:
- Notification: You may need to notify the Environment Agency and local authority before decommissioning.
- Oil Removal: All remaining oil must be removed by a licensed waste carrier.
- Tank Cleaning: The tank must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any residual oil or sludge.
- Disposal or Making Safe: The tank can be removed or made permanently unusable in situ.
- Documentation: Detailed records of the decommissioning process must be kept.
Information particularly in relation to underground tank decommissioning can be found at: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/prevent-groundwater-pollution-from-underground-fuel-storage-tanks/decommissioning-an-underground-storage-tank
Preventing spills is crucial for commercial oil storage. Best practices include:
- Bunded Tanks: Using bunded tanks or other forms of secondary containment.
- Leak Detection: Installing leak detection systems to provide early warning of a leak.
- Regular Inspections: Conducting regular inspections of tanks, pipework and valves.
- Staff Training: Training staff on proper handling procedures and spill response.
- Spill Kits: Keeping spill kits readily available in case of an incident.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of all tank components.
OFTEC (Oil Firing Technical Association): This is a key resource for heating oil tank guidance and best practices in the UK: https://www.oftec.org/
Maintaining fuel quality is essential for efficient operation and preventing equipment damage. Key considerations include:
- Regular Testing: Regular fuel testing to check for contamination (water, sediment, microbial growth).
- Filtration: Using appropriate filtration systems to remove contaminants.
- Storage Conditions: Store oil in a cool, dry place to prevent degradation.
- Supplier Quality: Choosing a reputable fuel supplier who provides high-quality oil.
- Additives: Consider using fuel additives to improve stability and prevent microbial growth (consult with a fuel specialist, such as JWH).
Nationwide Commercial Tank Services
From Scotland to Cornwall, JWH Tanks delivers top-tier commercial tank services throughout all areas of the UK. Our commitment to nationwide coverage ensures that businesses everywhere can access our expertise. Our coverage includes: